The Impact of Stem Cell Therapy Procedures on Congestive Heart Failure in Clinical Trial Patients
Yendelela Cuffee, Rishitha Guddapalli
1*Department of Epidemiology, University of Delaware, Delaware, United States
2MOT Charter High School, Delaware, United States
* Corresponding Author
E-Mail: ylcuffee@udel.edu
Word Count: 3502 words
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Conflicts of Interest: All authors declare no conflicts of interests
Abstract
Congestive heart failure is a health issue that over 6.7 million people experience just in the United States, and it has become a global pandemic, making it a leading cause of death. The latest methods, such as stem cell therapy, have had exceptional results on patients during clinical trials and reviews mentioned in this study. The research question being addressed is: What is the current research on stem cell therapy, and how do clinical trials reveal information about this treatment? The purpose of this study is to summarize the current understanding of stem cell therapy on congestive heart failure and its overall effect on patients as examined in clinical trials and data. The search method carried out was research papers that were examined and extracted to be written about in an annotated bibliography. Inclusion criteria included publication date, sample size, and relevance/accuracy of the information. A key trend throughout all sources was that stem cell therapy had an overall positive effect in mitigating heart failure and improving the lifestyle of patients. There is a reduced risk of getting a stroke or heart attack when stem cell therapy is prescribed. The results successfully answer the research question, and the presented research is significant to the current field’s understanding because it shows that stem cells have a positive turnover on heart failur,e and the study provides a more general understanding of this medical advancement, providing added credibility and advancing of current knowledge of stem cells.
Keywords: Congestive Heart Failure, Stem Cell Therapy, Stroke, Heart Attack, Stem Cells
Introduction
Background and Context
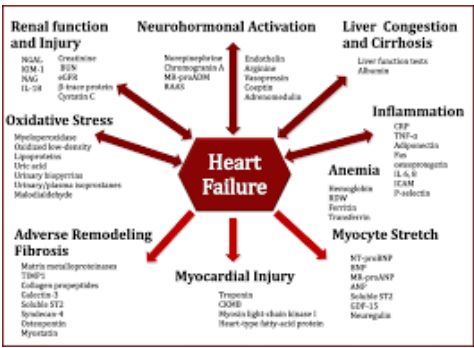
Cardiovascular disease and several other disorders like congestive heart failure are a leading cause of death in America and all over the world. 48% of adults in the US alone have cardiovascular disease (American Heart Association News, 2019)1. Cardiovascular disease is a group of diseases that affect the heart and its blood vessels and includes diseases such as heart failure, stroke, arrhythmia, and heart attack. These diseases can affect the cardiovascular system by damaging the structure of the heart and vessels or causing blood clots. This study focuses on congestive heart failure. Specifically, heart failures like chronic heart failure, where the heart cannot pump effectively, or diastolic heart failure, where the left ventricle of the heart cannot relax normally. These classifications of the disease are what stem cell therapy is tailored toward and can specifically treat. Congestive heart failure is when the heart simply cannot pump or fill enough blood for the body. Several hallmarks of congestive heart failure are dyspnea, raised jugular venous pressure, and peripheral edema (Ashley & Niebauer, 2004)2. This disease progressively degenerates the heart's myocardial tissue. The extra work performed by the heart can damage or weaken its muscle walls. Reduced cardiac output due to weakened muscles can lead to impairment in the left ventricle of the heart. This will cause an activation of the neuro-hormonal system, therefore stimulating increased concentrations of renin, angiotensin II, and aldosteron,e which all cause salt and water retention, vasoconstriction, and enhanced sympathetic activity. Salt and water retention occurs when there is excess fluid in the body and outside of the cells. Vasoconstriction is when the blood vessels of the heart are narrow, constricting or blocking blood flow. Overall, prolonged exposure to the neuro-hormonal activation system leads to structural changes in the heart and myocardium, therefore further worsening the existing conditions (Shrivastava et al., 2020)3.
Figure 1: Hallmarks & Effects of Heart Failure (Holzhauser et al., 2018)
Stem cell therapy, which is also known as regenerative medicine, uses stem cells to treat and repair damaged tissues or disease cells in a part of the body or a specific organ. With stem cells, doctors hope to regenerate healthy tissue and treat diseases, including congestive heart failure, which can treat diseased heart cells. Stem cells have unique properties where they can self-renew/replicate and differentiate into specific cell types depending on the location and the body’s needs. More specifically, stem cells differentiate by turning on or off specific genes. Some areas where stem cell therapy is widely used are for blood cancers, where bone marrow transplants are frequent treatments for leukemia, lymphoma, and more. Stem cells can be found in bone marrow, so this procedure is also a type of stem cell procedure. Other ways it has been used was by treating leading causes of blindness and severe burns on the body. Cardiovascular diseases such as congestive heart failure continue to take the lives of many people all over the world. However, new advancements are always developing in this rapidly developing field, affecting the current treatment and diagnosis of congestive heart failure cases. One such advancement is stem cell therapy for heart failure. Stem cells are a specific type of cells that can make more cells like themselves by dividing (Mayo Clinic, 2019)4. These cells can perform different tasks through differentiation, therefore, rebuilding tissues. Sometimes, stem cells can be used for maintaining or rebuilding tissue in cases of repair or injuries. Stem cells can become other types of cells, such as brain cells, heart muscle cells, and more. There are many types of stem cells, but when treating heart disease or heart failure, both embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells can be harnessed for heart tissue cells. Embryonic stem cells come from embryos that are 3 to 5 days old. At this stage, an embryo has about 150 cells, and these cells can perform differentiation to repair diseased organs like the one in heart failure (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2024)5. On the other hand, induced pluripotent stem cells are derived from skin or adult somatic cells that have been reprogrammed to be in an embryonic-like pluripotent state through inducing genes. Induced pluripotent stem cells are also similar to embryonic stem cells, therefore yielding great promise in unlimited expansion and differentiation when it comes to regenerating diseased organs.
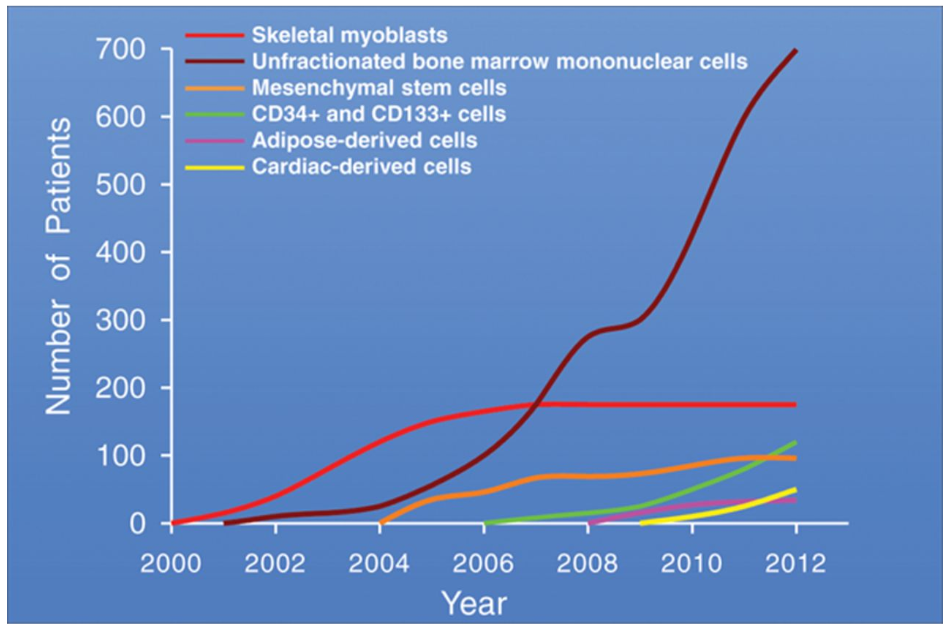
Figure 2: Sources of stem cells used for cardiac repair (Sanganalmath & Bolli, 2013).
Problem Statement and Rationale
The objective of this manuscript is to examine the current research done on stem cell therapy in the treatment of congestive heart failure and how recent clinical trials reveal the procedures and efficacies of this upcoming treatment.
Several clinics and institutions have researched to understand the latest research on stem cell therapy and its effectiveness on congestive heart failure. Overall, research has shown that stem cells improve heart function, reduce the risk of heart attack, and improve quality of life. A clinical trial at the Texas Heart Institution found that mesenchymal precursor cells, also known as MPCs, improved the heart’s pumping ability and reduced the risk of heart attack and stroke (Sprung, 2023)6. Mesenchymal stem cells are multipotent cells that can differentiate into several cells, like bone cells, tissue cells, and other types of tissues/organs. These cells are found in bone marrow and mesenchymal tissues.
In addition, a Mayo Clinical Trial found that stem cell therapy for heart failure improved quality of life for patients with advanced heart failure, like patients reporting less daily hardship and lower rates of mortality and hospitalization. Mayo Clinic researchers discovered these trends when they worked with international collaborators and conducted a large-stage multinational clinical trial. In this large study that focused on cell intervention after a heart attack, patients reported that they experienced less daily hardship when stem cells were used for heart repair rather than standard care. This study had 315 patients from 39 hospitals in 10 countries. The process implemented was the population was divided where some received stem cell therapy and some did not. This is classified as a randomized study because the clinical trial was conducted in a double-blinded fashion where the patients and doctors wore masks during the study assignment to reduce the risk of bias and minimize as few interventions as much as possible. Patients who were assigned stem cell therapy received cardiac catheterization, where stem cells were taken from their bone marrow and sent to the heart where they could repair damaged tissue. So far, this is the current research and major findings that have been discovered regarding this treatment for heart failure (Buckles, 2023)7.
The field of stem cell research geared towards heart failure is worth investigating and is highly relevant due to the many advancements it holds and the curative/personalized treatment it offers for heart failure patients. Most importantly, stem cell therapy has the potential to regenerate damaged heart muscle tissue. Heart failure has limited treatment and is a deadly disease that takes the lives of many patients. Still, this treatment can potentially replace dead heart cells with good ones, improving the heart and overall lifestyle of the patient. Despite the several benefits and relevance of stem cell therapy and heart failure, there are still research gaps, and the science is continuously evolving according to new findings. Ethical problems regarding stem cell therapy are an important issue that challenges this advancement, specifically in the use of embryonic stem cells. Another research gap is that more data and findings have to be established to analyze the long-term effects stem cell therapy has on a heart failure patient (Langmaid, 2017)8. More research is necessary to understand the long-term benefits and efficacies of this new procedure.
Significance & Purpose
Stem cell therapy in the regeneration of congestive heart failure has become a promising area of research in the field of myocardial biology. This latest advancement has been prioritized as significant due to its positive results in patients and clinical trials. One of the largest studies of cell intervention in heart attacks showed that patients reported their daily hardships to decrease when treated with stem cells rather than standard care for heart disease. Overall, stem cell therapy for heart failure documented lower mortality and hospitalization rates, further increasing its importance to research this promising medical advancement.
There is a documented need and interest in researching stem cell therapy for heart failure because it is increasing understanding of how disease occurs and how the heart degenerates specifically in heart failure. Also, stem cell therapy is helping test new drugs and medications for safety and effectiveness. For instance, before giving out drugs in development to people, researchers can use some types of stem cells to test for drugs’ safety and quality. This type of testing may help determine which drugs are toxic to the heart. Lastly, a significant need to further research this area is due to its relation to regenerative medicine. The purpose of this study was to explore the current research examining stem cell therapy for individuals with congestive heart failure and to determine the procedure for stem cell therapy and the benefits of the treatment.
Figure 3: Use of various types of stem cell therapies in patients with cardiovascular disease (Sanganalmath & Bolli, 2013).
Objectives
The specific objectives of the study are to understand and review the current research being done on stem cell therapy for heart failure and to examine how the clinical trial data reveal information regarding the efficacies and benefits of stem cell therapy. The research also aims to understand the different procedures carried out when performing stem cell therapies and reviewing data from clinical trials through systematic reviews and meta-analysis reports.
Methodology Overview
The overall methods that were employed to extract sources/data were to first create systematic search criteria. The search strategy was narrowed down, and specific sources were extracted, which were then recorded and explained in an annotated bibliography. Inclusion and exclusion criteria, including the publication date, credibility, and bias, were observed and recorded in the bibliography. The scope of research was identified to accurately narrow down information and extract the most relevant sources. These sources were used throughout the research investigation since they were directly relevant to the topic.
Methods
Search Strategy
The search strategy and systemic approach implemented was to first understand the basics of cardiology, stem cell therapy, and sub-concepts in general. Building a knowledge of the fundamental topics created a great impact in understanding the more complex topics regarding these major fields. First, digital notes and information were written down regarding the basics of the topic. After this step was over, the official research for understanding the actual topic of heart failure and its treatment of stem cell therapy began. Databases like the Google search engine and the PubMed database were utilized to search for research papers and systematic/meta-reviews on the web. Occasionally, Google Scholar web and Scholarly papers were analyzed through the Google search engine. After analyzing the different sources and research works, the most important and relevant papers were chosen to be written in an annotated bibliography document. The criteria for selecting these papers included making sure the research was published in the last five years, includes a large-scale clinical study, and the bulk of the information written in the paper is very relevant to the research question and purpose of this paper. Other criteria included analyzing the source of the research paper, like what publication it belongs to and what websites it has been published on.
Inclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria for choosing these sources are analyzing how close the topic alignment is and identifying when the paper’s topic is as related as possible to the research question of the paper. Other criteria were scope and considering the depth of the paper and if the information is written in sufficient detail/specificity. The third biggest inclusion criteria were the publication date of the research paper and be ability to prioritize the most recent sources. Since the main research focus is advancements in the treatment of heart failure, the publication date and the accuracy of the information were heavily prioritized in the search strategy process. On the other hand, the exclusion criteria were avoiding overly broad topics, outdated sources that are older than 5 years, and only analyzing sources that were relevant to the research question and topic. Other ways that were used when filtering out sources were the popularity
Data Extraction
Specific sources were extracted by analyzing factors like relevance to the topic, key findings regarding stem cell therapy for heart failure, publication date, and overall credibility of the source. The credibility of the source/research paper was evaluated based on the author and their qualifications, the reputation of the publication site, if there is any bias in the paper, and the publication date of the paper. If the source has a direct correlation to heart failure and how stem cell therapy provides relevance to it, this source was chosen to be researched further. If a source mentions advancements particular to this field and changes being made to improve stem cells for heart failure, that source would also be used for further analysis since it directly gives information to research questions and studies. Lastly, the criteria for the publication date was for the source to be published in the last five years to gain the most recent findings about this evolving field. To define the scope of the study, the report includes explaining definitions of various topics and terms, analyzing clinical studies including meta-analyses, and interpreting the benefits of stem cells and the different stem cell procedures patients can go through to treat congestive heart failure. The current knowledge of heart failure, current treatments, future directions for this field, and the results of this review will be analyzed and conducted. Related topics like stem cell ethics and general stem cell applications will be excluded from the study. Constraints that were brought up while discussing and researching these topics include stem cell clinical trial limitations such as sample size and data limitations. Other constraints include finding bias in sources and former publications released more than ten years ago.
Synthesis Method
The gathered information and sources were organized and described in an annotated bibliography document. Five to eight relevant sources were extracted, and they were listed as APA formatted sources in an annotated bibliography. Each source was described in a paragraph in terms of the publication date, main findings within the source, relevance to the topic, and the credibility of the source. These sources in the bibliography were consistently used during the research and data extraction process.
Figure 4: Apparatus summarizing methods of research
Discussion
Key Findings
As stated before, the research question that is being investigated is what is the current research done on stem cell therapy in the treatment of congestive heart failure and how do recent clinical trials reveal procedures, and efficacies of this upcoming treatment? So far, several clinics and institutions have researched to understand the latest research on stem cell therapy and its effectiveness on congestive heart failure. Overall, research has shown that stem cells improve heart function, reduce the risk of heart attack, and improve quality of life. Clinical trials show that there is a clear reduced risk of heart attack and stroke when patients receive stem cell treatment. Stem cells have also been found to eliminate plaque buildup in the arteries, which is the main cause of issues like coronary artery disease and heart attack.
Implications and Significance
The findings presented in this study contribute to the stem cell field because they present the main finding that stem cell therapy has an overall improvement in heart failure. Although it does not cure it, it still improves patients’ lifestyle and their improvement of the disease. This academic significance of the study is one main way this study contributes to the current research field of stem cell therapy. This presented research advances existing knowledge because data already shows that stem cells have a positive impact on heart failure, so this research attempts to summarize these findings and provide a more general understanding of the effects of stem cell therapy on heart failure.
Connection to Objectives
All in all, the research objectives and the hypotheses were met. The research question is also successfully answered through the information presented. This is because the research question mainly asked the current research regarding stem cell procedures for heart failure. This part of the question was answered through several clinical trials that were mentioned along with their procedures and results. For instance, the Texas Heart Institution clinical trial mentioned before used mesenchymal precursor cells, also known as MPCs, to assess the heart’s pumping ability and understand the extent to which it can help treat congestive heart failure. The other part of the research question asks about the significance of these results and the clinical trials. Based on the Mayo Clinic trial done on a large sample of patients, the overall significance was that stem cell therapy has a positive effect on patients who received this treatment across the sources and clinical trials analyzed. Overall, the objectives and research questions proposed were met and answered.
Recommendations
Despite the positive effects that are tied to stem cell therapy, there are still some drawbacks and research gaps that have to be further addressed. For instance, one disadvantage of this procedure includes stem cells leaving the body quickly and their inability to function for long periods. Future research in this specific area should focus on how researchers can look for ways for stem cells to “stick” in the body. Other areas of research can work more on identifying which stem cells work best, how they should be handled before transplantation, and the best stem cell procedure specifically for heart failure. These are some areas that need more refinement and information to fill gaps and gain accurate results about the long-term effects of stem cells on patients diagnosed with congestive heart failure.
Limitations
Weaknesses that impacted the study mostly occurred in the methods and extraction of sources for research. Sometimes, sources were too general and not relevant to the research question or focus of the paper. Other weaknesses include not checking for bias in sources and not analyzing the generalizability or relevance of the research topic. Minor weaknesses include not expanding the scope of research by searching for more articles or having too many sources focused on one concept of the topic. These weaknesses might have impacted the study by affecting the reliability of its research and results. For instance, it could have made the information in the research paper less accurate and too broad. Another limitation might include that not all relevant sources extracted were included in the review, therefore not maximizing the amount of applicable information that could be assessed. Despite these limitations, the weaknesses had a minor effect on the reliability and significance of the research paper.
Closing Thought
As the world progresses and technologies advance, the prognosis and treatment of heart failure can be better estimated to improve human lives with technologies like stem cell therapy. With technological advancements also come ethical considerations, especially for stem cells and their proper use. Stem cell use should not only be restricted for the sake of research but should also consider the ethicality that comes with it and how this important health advancement affects the well-being of society.
Acknowledgments
A special thanks to Professor Yendelela Cuffee for her help through the editing, research, and writing process of this paper.
References
American Heart Association. (2024, January 24). More than half of U.S. adults don’t know heart disease is leading cause of death, despite 100-year reign. Retrieved from American Heart Association website: https://newsroom.heart.org/news/more-than-half-of-u-s-adults-dont-know-heart-disease-is-leading-cause-of-death-despite-100-year-reign
Ashley, Euan A., and Josef Niebauer. Heart Failure. Www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, Remedica, 2004, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2218/.
Shrivastava, A., Haase, T., Zeller, T., & Schulte, C. (2020). Biomarkers for Heart Failure Prognosis: Proteins, Genetic Scores and Non-coding RNAs. Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine, 7, 601364. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2020.601364
Mayo Clinic Staff. “Stem Cells: What They Are and What They Do.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 23 Mar. 2024, www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/bone-marrow-transplant/in-depth/stem-cells/art-20048117.
Sprung, Keri. “The Texas Heart Institute Delivers a New First in Heart Failure Treatment Using Cell Therapy.” The Texas Heart Institute, 27 Feb. 2023, www.texasheart.org/the-texas-heart-institute-delivers-a-new-first-in-heart-failure-treatment-using-cell-therapy/.
Buckles, Susan. “Clinical Trial Finds Cell Therapy Improves Quality of Life in Advanced Heart Failure.” Mayo Clinic News Network, 12 Dec. 2023, newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/clinical-trial-finds-cell-therapy-improves-quality-of-life-in-advanced-heart-failure/.
Langmaid, Stephanie. “Stem Cells for Heart Failure Treatment.” WebMD, WebMD, 18 Oct. 2017, www.webmd.com/heart-disease/heart-failure/stem-cells-heart-failure-treatment.